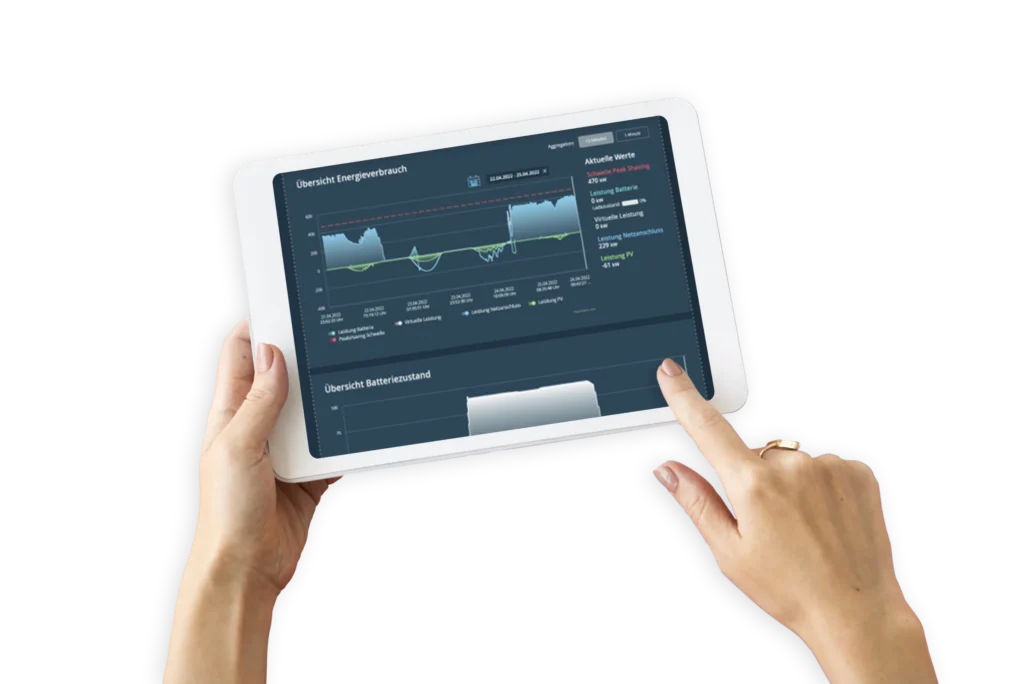
Intensive grid usage refers to the utilization of energy grids beyond their regular capacities. This practice can have both positive and negative effects on grid stability, especially during times of high demand or irregular feed-in of renewable energies. Effective management of intensive grid usage is therefore crucial for ensuring a stable and efficient energy supply.
Table of contents
ToggleFunctionality of intensive grid usage
Intensive grid usage requires dynamic management of loads in the grid. Especially in times of high demand or sudden changes in feed-in, grid operators must be able to react quickly to changes. Technologies such as smart grids and load management systems are used for this purpose, enabling flexible adaptation of energy flows. Companies
Causes of intensive grid usage
The causes of intensive grid usage are varied:
- High demand: Industries with high energy requirements can heavily strain grid capacities.
- Renewable energies: The irregular feed-in of renewable energies requires flexible grid usage.
- Technological developments: The use of new technologies can significantly increase energy demand.
- Electricity-intensive grid usage: Companies that reach at least 7,000 usage hours within a calendar year and have an annual electricity consumption of over 10 GWh can benefit from an individual grid fee. This can lead to a reduction in grid costs of up to 90 percent.
Consequences of intensive grid usage
- Grid stability: Overloads can lead to instability and power outages.
- Grid expansion: Inefficient grid usage can entail high investments in grid expansion.
- Financial implications: Companies may face higher costs if they heavily load the grid during peak times.
Strategies for optimizing grid usage
- Load management systems: Implementation of technologies that optimize energy consumption. These can particularly contribute to meeting the requirements of intensive grid usage and benefiting from reduced grid fees.
- Energy storage solutions: Use of battery storage to balance supply and demand.
- Demand Response programs: Incentives for companies to reduce their energy consumption during peak times.
Regulation and political framework
The regulation of grid usage is subject to various national and European regulations. Companies should inform themselves about the applicable provisions in order to design their grid usage efficiently and in compliance with the law.
Advantages and disadvantages of intensive grid usage
Advantages of intensive grid usage
- Efficiency increase: Effective usage can lower operating costs by benefiting from grid fee reductions.
- Grid stability: A constant power consumption ensures a stable supply.
- Integration of renewable energies: Flexibility in grid usage enables better integration of sustainable energies.
Disadvantages of intensive grid usage
- Risk of overloads: High loads can endanger grid stability, especially during peak times.
- Costs: The maintenance and expansion of grid infrastructures can be expensive.
Trends in intensive grid usage
The increasing digitalization and technological progress in the energy industry will further strengthen the role of intensive grid usage. Innovative solutions such as blockchain technologies and IoT applications offer new approaches to optimizing grid usage and improving grid stability.
Summary of intensive grid usage
Intensive grid usage is a complex topic that presents both challenges and opportunities for companies. Proactive management and the use of modern technologies are crucial for ensuring a stable and efficient energy supply. In addition, atypical grid usage should also be considered, as it offers specific requirements and opportunities for companies.
Note: Please note that this wiki entry on intensive grid use is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. be.storaged GmbH assumes no guarantee for the completeness, accuracy and timeliness of the information in this entry.