Control energy is a crucial component of the power grid, which serves to compensate for short-term fluctuations in electricity consumption and generation. In essence, control energy enables a rapid adjustment of electricity generation or consumption to maintain the balance in the power grid. Whenever the demand for electricity rises or falls or unexpected events occur, such as the failure of a power generation plant, control energy is used to keep the grid stable.
Table of contents
ToggleFunctionality of control energy
Control energy is a dynamic instrument that is used to compensate for unexpected fluctuations in the power grid and to keep the grid frequency stable. In contrast to planned power generation or consumption changes, control energy is provided in real time to maintain the balance between supply and demand. It enables grid operators to react flexibly to changes and to keep the power grid stable, even when unforeseen events occur.
Types of control energy
There are different types of control energy, which are distinguished according to their response time and availability:
- Primary control energy: This type of control energy reacts the fastest to changes in the power grid and is used to compensate for short-term frequency deviations. Typically, primary control energy is provided by fast and flexible plants such as hydroelectric power plants.
- Secondary control reserve: Secondary control reserve has a slightly longer response time than primary control reserve and is used to compensate for slower changes in the power grid. It ensures that the grid frequency remains within a narrow tolerance range and that larger fluctuations in the power grid are avoided.
- Tertiary control power (minute reserve): This type of control reserve has the longest response time and is used to compensate for long-term imbalances in the power grid. Tertiary control reserve is typically used for planning and forecasting electricity demand and generation in order to ensure long-term stability in the power grid. The tertiary control reserve is often referred to as the minute reserve because it is activated within a few minutes to correct longer-term deviations.
Actors in the control energy market and their role
There are various actors in the control energy market who play an important role in its provision and use:
- Transmission system operators (TSOs): The transmission system operators are responsible for the planning, operation and security of the power grid. They coordinate the use of control energy to maintain the balance between supply and demand and to ensure grid stability.
- Control energy providers: These companies provide control energy by flexibly controlling their power generation plants or consumer facilities. Control energy providers can operate both conventional and renewable energy plants and play an important role in ensuring grid stability.
- Control energy marketers: These companies trade in control energy and bring supply and demand together on the control energy market. They organize auctions and contracts for the supply of control energy and ensure that the power grid remains stable at all times.
- Consumers: Consumers can also play a role in the control energy market, especially if they have flexible loads. By being able to adjust their electricity demand, consumers can contribute to the stabilization of the power grid and potentially benefit from the provision of control energy.
Benefits of control energy
The use of control energy offers a variety of benefits for the power grid and the energy industry as a whole:
- Grid stability: It helps to ensure grid stability by compensating for short-term fluctuations in the power grid and stabilizing the grid frequency.
- Efficiency: Through its use, transmission losses can be minimized and the efficiency of the power grid can be improved.
- Flexibility: It enables grid operators to react flexibly to changes in electricity consumption and generation and to adapt the power grid to different conditions.
- Integration of renewable energies: It plays an important role in the integration of renewable energies by compensating for their fluctuations in the power grid and ensuring a reliable power supply.
Challenges and solutions
Despite the advantages, there are also challenges that need to be overcome in order to exploit its full potential. These include the complexity of the control energy markets, the integration of large quantities of renewable energies and the need for improved grid infrastructure. However, by developing and implementing innovative technologies and business models, these challenges can be successfully overcome.
Summary
Control energy is indispensable for grid stability and the balance between electricity supply and demand. Important players here are transmission system operators, control energy providers and marketers, and consumers. The benefits of using control energy include grid stability, efficiency, flexibility, integration of renewable energies and economy.
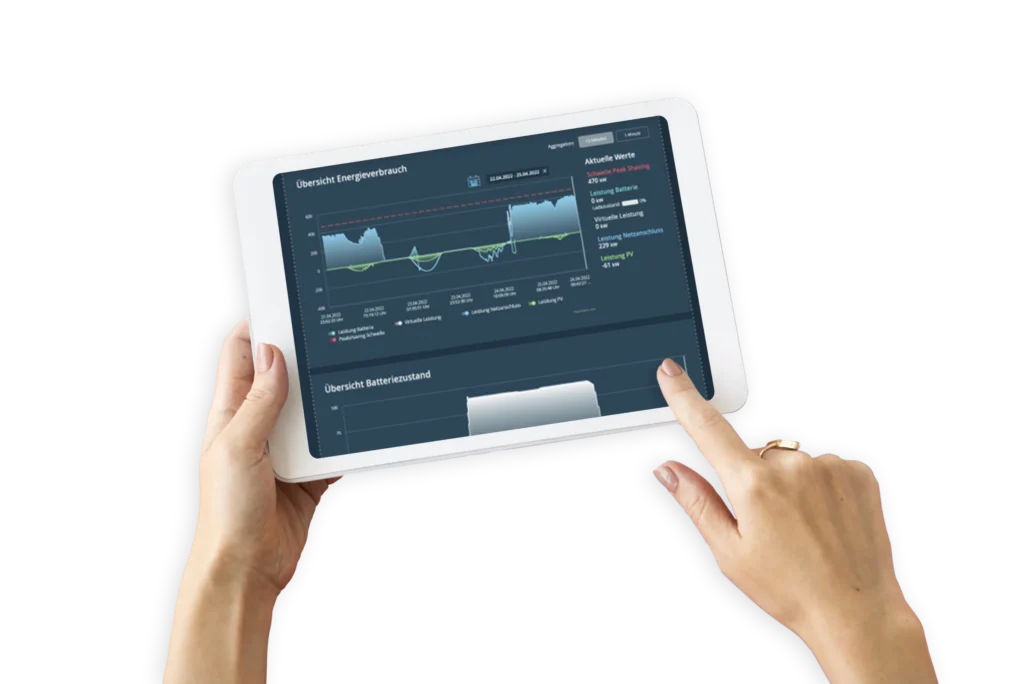
Additionally, energy management and battery storage solutions significantly contribute to supporting reserve power. Effective energy management improves the coordination of consumption and generation, while battery storage stores surplus energy and feeds it into the grid when needed. This facilitates the integration of renewable energies and increases grid stability.
Innovative energy solutions such as smart grids and virtual power plants further optimize the electricity grid by utilizing advanced technologies to dynamically adjust supply and demand and efficiently manage decentralized energy sources. Overall, these measures improve the sustainability and economic efficiency of the energy supply.
Note: Please note that the wiki entry control energy is for information purposes only and does not replace legal advice. be.storaged GmbH assumes no guarantee for the completeness, accuracy and timeliness of the information in this entry.